Urinary Tract Infection Symptoms, Risk Factors & Treatment | Diseases List A-Z
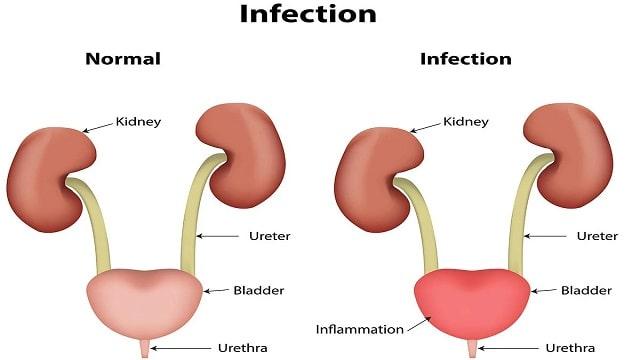
Urinary Tract Infection Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a condition when the urinary system experiences an infection.
It can be in the ureter, kidney, bladder, and urethra.
Generally, the infection attacks two parts, namely the urethra and the bladder.
Although it can happen to anyone, this infection is more likely to occur in women.
In addition, this infection can attack deeper parts and the most common one that occurs is a bladder infection (cystitis).
Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infections in Women and Men UTIs can cause the lining of the urinary tract to become red and inflamed (irritated).
Some of the characteristics of UTI that can occur in men and women include: 1.
Characteristics of Urinary Tract Infections in Women Symptoms of urinary tract infections in women can include: Pain or burning sensation when urinating.
More frequent urination.
Urine smells and has a different color than usual.
Pelvic or lower abdominal pain.
Feeling weak and unwell.
Fever.
Shivering.
Bloody urine (hematuria).
In girls, they tend to be restless or cry when urinating.
2.
Characteristics of Urinary Tract Infections in Men Although more common in women, men can also experience urinary tract infections (UTIs) with the following symptoms: Pain or burning sensation when urinating.
Difficulty urinating.
Frequent urination.
Pain in the lower abdomen or lower back.
Urine smells and is colored differently than normal.
Fever.
A feeling of discomfort in the pelvic or genital area.
Exhaustion.
Intense pain.
Risk Factors for Urinary Tract Infections General risk factors for urinary tract infections include: Have urinary tract abnormalities.
Having a blockage in the urinary tract.
Have a low immune system.
Using a catheter.
Having surgery or a urinary tract examination.
This disease is more common in women, and many women experience it more than once during their lifetime.
Several factors that increase the risk of this disease in women, namely: Sexually active.
The anatomy of the female body has a shorter urethra than men.
Using certain types of contraception.
Already menopausal.
Women who have the habit of wiping the genital area after urinating from back to front are also at risk of contracting this disease.
This is because the urethra is located close to the anus which tends to have a lot of bacteria.
Sexual intercourse can also cause bacteria to enter the urinary tract, apart from dirty habits after urinating.
Therefore, cleaning the genital area after having sex is very important.
Types of Urinary Tract Infections UTIs are divided into several types, depending on which part of the urinary tract is infected.
Some common types are: Urethritis.
Infection of the urethra, the hollow tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
Cystitis.
A bacterial infection of the bladder that often spreads from the urethra.
Pyelonephritis.
This occurs in the kidneys, usually due to an infection that has spread to the urinary tract, or from a blockage in the urinary tract.
Obstruction in the urinary tract causes urine to flow back into the ureters and kidneys.
Causes of Urinary Tract Infections The cause of urinary tract infections is bacteria that infect one part of the urinary system.
The type of bacteria that most often causes this infection is E.
coli.
However, there are several other types of bacteria that can also cause UTIs.
Such as Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, and Staphylococcus saprophyticus.
This disease can occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra and grow in the bladder.
Although the urinary system works to prevent bacteria from entering through the urethra, sometimes it can still happen.
Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infection Some tests and procedures to diagnose urinary tract infections, namely: Urinalysis.
Examination of a urine sample, looking for white blood cells, red blood cells, or bacteria.
Urine Culture Examination.
This is useful to determine the type of bacteria present, in order to determine the right treatment.
Imaging tests.
Such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI, to see images of the urinary tract.
Cystoscopy.
An examination using a special instrument inserted through the urethra to look inside the bladder.
Urinary Tract Infection Treatment The most common treatment for this disease is by administering antibiotics.
This drug is able to kill bacteria, thereby eliminating the infection that occurs.
However, make sure to finish the antibiotics according to the doctor’s prescription so that the bacterial infection is resolved and the body does not become resistant to the drug later.
In addition, it is also necessary to consume more water so that bacteria can be removed from the urinary tract system.
So, Can Urinary Tract Infections Be Cured with Pipemidic Acid? If this condition recurs three times in a year or more, ask your doctor to recommend a specific treatment plan.
Some treatment options that you can undergo include: Using low doses of antibiotics over a longer period to help prevent recurrent infections.
Taking a single dose of antibiotics after intercourse, to prevent common triggers of infection.
Take antibiotics for 1 or 2 days whenever you feel symptoms.
So, if you experience bladder problems, contact this doctor immediately.
Recommended Medications for Treating Urinary Tract Infections The following are recommended medications for treating urinary tract infections: Floxifar 500 mg 10 Caplets.
Tablets containing the antibiotic Ciprofloxacin which are useful for treating infections in the urinary tract, bones and joints, and digestive tract.
Scopma 10 mg 10 Caplets.
Used to treat stomach pain or serious digestive disorders.
Spasmolit 10 mg 10 Tablets.
A hard drug that can be consumed based on doctor’s instructions.
This drug contains Hyoscine Butylbromide to treat digestive disorders such as paroxysmal pain in the stomach or small intestine.
Tequinol 500 mg 10 Caplets .
Can be consumed to treat severe infections caused by bacteria such as urinary tract infections, urethritis, and infections of the digestive tract and respiratory tract.
Baquinor Forte 500 mg 10 Caplets .
Antibiotics containing Ciprofloxacin are useful for treating infections of the urinary tract, skin and soft tissue, bones and joints, to acute osteomyelitis.
Helixim Dry Syrup 30 ml.
Is a type of antibiotic that contains Cefixime to treat urinary tract infections without complications.
Cefspan Dry Syrup 30 ml.
With Cefixime content, this drug is an antibiotic to treat urinary tract infections, pharyngitis, and tonsillitis.
Buscopan 10 mg 10 Tablets .
Tablets containing Hyoscine-N-butyl bromide are useful for treating spastic disorders in the digestive tract, urinary tract, bile duct, and genital tract in women.
Prive Uricran 10 Capsules .
Supplements that contain multivitamins and Isoflavones that are useful for maintaining urinary tract health.
Complications of Urinary Tract Infections Urinary tract infections that are not treated immediately can trigger urosepsis, a condition where bacteria in the infected kidney spread to the blood.
This causes many bad effects, such as shock and even death.
In addition, in some cases this disease can also cause: Premature birth, if this disease occurs in pregnant women.
Permanent kidney damage if the bacteria spread to the kidneys.
Narrowing of the urinary tract.
Prevention of Urinary Tract Infections Here are some efforts to prevent urinary tract infections: Not holding urine.
Always clean the genital area from front to back after urinating.
Drink plenty of water.
You should avoid feminine hygiene sprays, feminine fragrances, and other products for the feminine area because they will only irritate the mucosa.
Clean the genital area before having sex.
After intercourse, urinate.
This is to remove any bacteria that may have entered the urethra.
Don’t wear underwear for days.
Do not wear tight bottoms as they will increase humidity.
.
Related Articles
health
Aquaphobia Symptoms, Risk Factors & Treatment | Diseases List A-Z
October 22, 2024

Aquaphobia is a type of specific phobia that is an irrational fear of something that does not pose much danger.
A person with aquaphobia has extreme fear or anxiety when thinking about or seeing water.
read morehealth
Arrhythmia Symptoms, Risk Factors & Treatment | Diseases List A-Z
October 22, 2024
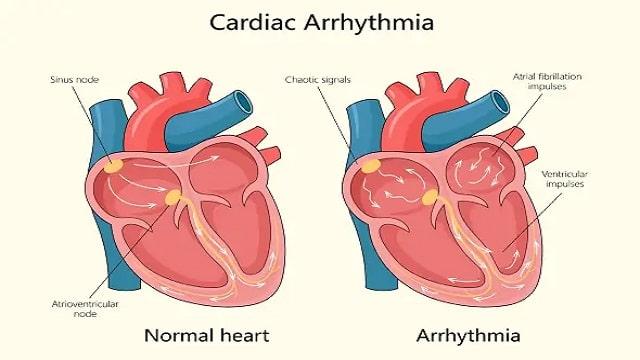
Electrolyte imbalance in the blood.
Electrolyte levels, such as potassium, sodium, calcium, and magnesium can interfere with the heart’s electrical impulses, resulting in arrhythmias Drug use.
read morehealth
South Africa: Over 40 students hospitalised for suspected food poisoning
October 23, 2024

The information contained in this website is for general information purposes only.
The information is provided by BhaskarLive.
read more