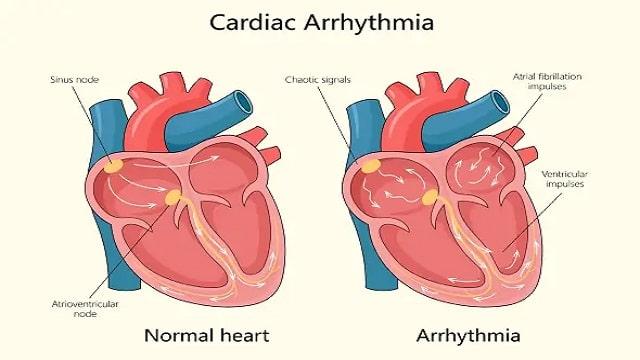
Arrhythmia Symptoms, Risk Factors & Treatment | Diseases List A-Z
Electrolyte imbalance in the blood.
Electrolyte levels, such as potassium, sodium, calcium, and magnesium can interfere with the heart’s electrical impulses, resulting in arrhythmias
Drug use.
Illegal drug use can affect how your heart works, increasing your risk of this condition.
Medication side effects.
Some over-the-counter cough and cold medications can increase a person’s risk of developing arrhythmia.
Drinking a lot of alcohol.
Excessive alcohol consumption can affect the heart’s electrical impulses, increasing the risk of arrhythmia.
Consuming a lot of caffeine or nicotine (smoking).
Caffeine and nicotine cause the heart to beat faster than normal, resulting in arrhythmia.
Thyroid disorders.
An overactive or underactive thyroid gland can increase the risk of arrhythmias.
Obstructive sleep apnea.
In this condition, the breathing experienced by sufferers of this disease will be disturbed during sleep which can increase the risk.
Diabetes.
Uncontrolled diabetes can increase the risk of coronary heart disease, high blood pressure, and arrhythmias.
Hypertension or high blood pressure.
Hypertension can cause the left ventricle wall of the heart to thicken and become stiff so that the electrical flow of the heart is disturbed.
Coronary heart disease, other heart disorders, or a history of heart surgery.
Narrowing of the coronary arteries, heart attack, heart valve abnormalities, heart failure, and other heart damage are risk factors for almost all types of arrhythmias.
.